What is Prostate Cancer? Risk factors, Preventions, Types, and How Dr Sandeep Nunia can help you to cure it.
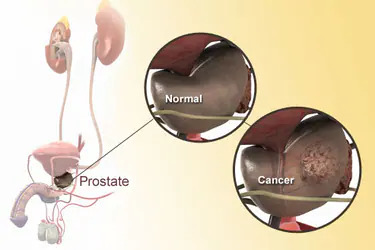
Prostate cancer is primarily found in men’s prostate glands. The prostate gland produces the seminal fluid that nourishes & transports the sperm. The cells of the prostate grow in an uncontrollable manner that causes tumour in the prostate. Prostate cancer is treatable if detected at early stages. If you have prostate cancer, consult Dr Sandeep Nunia, as he is the best urologist in Jaipur.
Let’s understand the risk factors, types, causes, symptoms and prevention of prostate cancer.
Tumour/ Cancer develops in a body when the cell begins to grow out of control. This growth of cells in any part of the body can become a tumour and spread to other organs if not treated early. The prostate gland is only found in men & men of age 50+ generally suffer this cancer.
Types of prostate cancer:
The following are the various types of prostate cancer-
1. Acinar adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is cancer that develops in the prostate gland. This is the most common type of prostate gland.
2. Ductal adenocarcinoma
Ductal adenocarcinoma is cancer that starts in the tube of the prostate gland. It spreads in the other organ fast as compared to acinar adenocarcinoma.
3. Transitional cell (urothelial cancer)
This cancer cell grows in the tube (that carries urine to the urethra). This cancer starts in the urethra and then spreads into the prostate gland.
4. Squamous cell cancer
Squamous cell cancer develops from flat cells that cover the prostate. They grow & spread more quickly than other prostate cancer.
5. Other types of cancer
Prostate cancer can be of more types that are as follows-
- Small cell carcinomas
- Neuroendocrine tumours
- sarcomas
Some of the prostate tumours have quick growth, while some grow slowly.
What causes Prostate cancer?
There is no exact cause of prostate cancer, but according to research, the changes in the DNA of normal prostate cells can cause prostate cancer. There are specific genes present in the body that help grow the cells and divide that are called oncogenes.
Suppressor genes keep the growth of the cell in control and repair the DNA mistakes. It helps to kill the cells.
DNA mutation can cause cancer that keeps the oncogenes adapted and turning off tumour suppressor genes leading to unwanted cell growth. The change in the DNA can be inherited from the parent (heredity) or can be procured during a person’s lifetime.

Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer:
The following are the risk factors for prostate cancer.
- Older age
- Ethnicity/Races
- Gene changes
- Family background
- Obesity
- Inflammation of the prostate
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Vasectomy
- Unhealthy diet plans
- Smoking
- Chemical exposures
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented?
Yes, prostate cancer can be prevented. The risk factor of age, race or family background cannot be controlled, but one can avoid prostate cancer by adopting good & healthy habits.
Prevention for prostate cancer
- Eat a healthy & nutrient-rich diet that is full of fruits & vegetables
- Regular exercise
- Maintain a healthy weight as obesity can cause many diseases
- Consult immediately if you are facing any signs of prostate cancer
Who treats prostate cancer?
- A urologist or Uro-oncologist is the person or doctor who treats prostate cancer. A urologist delivers the treatment for any urological diseases.
Dr Sandeep Nunia specialises in treating diseases of the urinary system and male reproductive system if you are looking for the best urologist.
- Radiation oncologist: radiation oncologist is a specialist who treats prostate cancer with the help of radiation therapy
- Medical oncologist: Medical oncologist is a specialist who treats prostate cancer with chemo, hormone, medicine and immunotherapy
Treatment for localised Prostate cancer:
The following are the treatment available for localised prostate cancer-
- Radical prostatectomy- is the procedure or surgery to remove the prostate tumour for the prostate gland. This treatment is given only when the tumour has not spread yet, and it is only in the prostate. Radical prostatectomy include the following surgeries-
- Open surgery
- Laparoscopic surgery
- Robotic surgery
- Radiotherapy- Radiotherapy is an effective procedure to kill prostate cancer. The high energy rays or particles are used to kill the tumour in the prostate gland.
Treatment for Locally advanced Prostate cancer:
The following are the treatment available for locally advanced prostate cancer-
- Radiation therapy with Hormonal therapy- Hormone therapy is the procedure to stop the body from making testosterone or to stop testosterone from reaching the cancer cells.
- Metastatic (Advance) Cancer Prostate: This treatment is given when the tumour starts spreading to other organs of the body. Metastatic (Advance) Prostate cancer treatment include the following-
- Hormonal therapy- Hormonal therapy includes-
- Abiraterone
- Enzalutamide
- Chemotherapy