
What is Urinary Tuberculosis?
Urinary Tuberculosis is bacterial contamination brought about through Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli. Bacteria may enter the lungs from the air. If our body fails to resist the bacteria it can attack any part of the body. They can additionally unfold via the bloodstream and settle and enhance wounds in any phase of the body. Tuberculosis which is most common in the lungs can affect nearly any section of the body. The contamination of the urinary tract begins in the kidney. It can then go to the ureter and urinary bladder.
How ordinary is Urinary Tuberculosis?
There are a total of 9.1 million cases out of it cases in India are 1.4 million In the whole world.
Who is at the risk for Urinary Tuberculosis?
Urinary Tuberculosis is frequently found in aged people from 20-40 years. Women have a somewhat higher predominance than men. It’s also frequent in patients with immune deficiency syndrome, diabetes, and those who are malnourished.
How does Urinary Tuberculosis affect our kidneys?
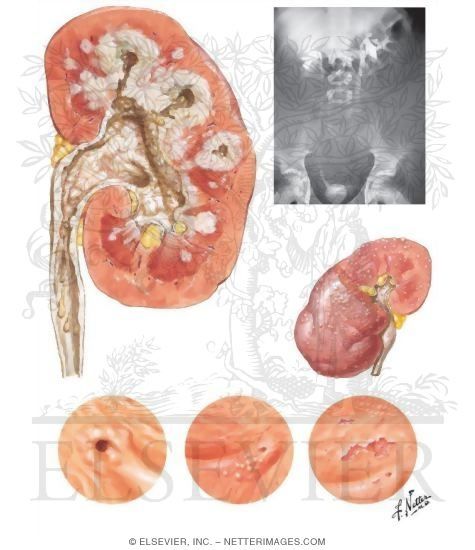
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis destroys kidney tissue, causing ulceration and the creation of granulomas. It starts in the calyces and subsequently spreads to other areas of the kidney, such as the parenchyma and renal pelvis. The ulceration eventually heals through fibrosis, which can lead to a constriction known as a stricture.
It can impact urine drainage from the kidney at several levels, including calyces (hydrocalyx), kidney outlet narrowing (pelvic ureteric junction obstruction), and ureteral lumen narrowing (ureteric stricture). Kidney function can be gradually decreased when the drainage system narrows. If the infection arises within the blocked system (pyelonephritis), the kidney’s function will be lost more quickly.
When an infection affects the bladder, it can lead to ulceration of the mucosa lining, producing significant pain when urinating. Due to fibrosis, the bladder’s capacity can eventually diminish, resulting in frequent urination.
Are Genitals being affected?
It can affect the epididymis (the cap-like structure that covers the upper part of the testis) and, in rare cases, the testis itself. Prostate and penis involvement are extremely uncommon.
Symptoms of Urinary Tuberculosis:-
1. Frequent urine as well as painful urine
2. Groin pain
3. Fever
4. Lower abdomen pain
5. Blood in urine
6. Scrotal pain
7. Swelling of the epididymis
8. Reduced urine flow.
What method is used to make the diagnosis of urinary tuberculosis?
Because clinical signs are frequently ambiguous, a high index of suspicion is required to make an early diagnosis. The presence of pus cells in the urine, the absence of bacterial development (sterile pyuria), and the detection of TB bacteria on smear testing are all important tests that help to confirm the diagnosis. Urine for gene Xpert and a CT scan can aid with the diagnosis even more. In the early stages of the disease, cystoscopy can reveal the presence of ulcers, whereas, in the later stages, it can reveal diminished bladder capacity. A biopsy of the ulcerated area will reveal the existence of granuloma, which is characteristic of tuberculosis.
Difficulties that can occur?
Kidney failure is caused by a blockage in urine drainage, infection, or total renal parenchymal destruction.
How can these difficulties be cured?
The mainstay of treatment is chemotherapy using anti-tuberculosis medicines. It should be given for a long enough duration, often 6 to 9 months. Drug therapy should be administered regularly, with good follow-up.
Is surgery required for urinary tuberculosis treatment?
The obstruction of urine drainage at various levels will necessitate surgery. The kidney may be removed in rare cases, but only if the kidney is completely ruined. The bladder’s capacity can be increased by utilizing bowel segments if it has diminished.
Key points which are to be taken care of:-
The signs of urinary incontinence should not be overlooked.
Take your medication as directed and see your doctor regularly.
Genito-urinary TB is treatable and has a fair prognosis.